Fatty liver disease is becoming a major health issue around the world, affecting millions of people. This condition happens when too much fat builds up in the liver cells. If not treated, it can cause inflammation, damage to the liver, and may even lead to severe problems like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
The good news is that fatty liver disease can often be managed with simple lifestyle changes. One of the most effective ways is through a proper fatty liver diet. Eating the right foods can help reduce fat in the liver, lower inflammation, and improve liver function over time. It’s important to focus on healthy choices and avoid foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and processed ingredients.
A fatty liver diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. By making these dietary changes, people can support their liver health and possibly reverse the effects of fatty liver disease.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about fatty liver disease and the best dietary approaches to combat it. We will also introduce the top 8 fatty liver diets that have proven effective in supporting liver health.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
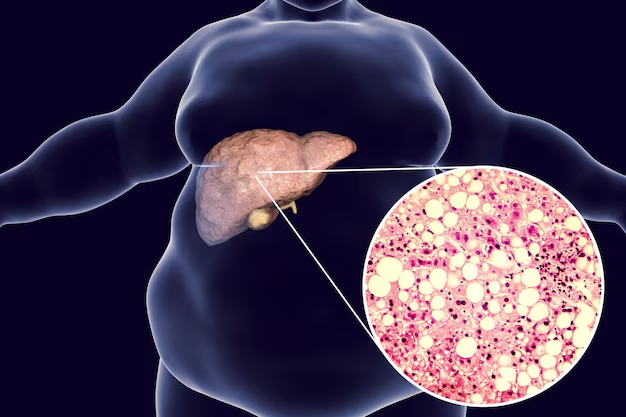
What is Fatty Liver ?
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, happens when too much fat gathers in the liver cells. This condition is becoming more common due to unhealthy eating habits and a sedentary lifestyle.
If not managed properly, fatty liver disease can lead to liver inflammation, scarring, or even serious liver damage over time. Early lifestyle changes are important to help reduce liver fat and improve overall health.
One of the best ways to manage this condition is by following a proper fatty liver diet. This includes eating more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while avoiding sugary, fried, and processed foods. A healthy diet can support the liver and may even reverse early signs of fatty liver disease.
There are two main types:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Fat buildup not related to alcohol consumption. Linked to obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and poor diet.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease: Caused by excessive alcohol intake.
NAFLD is the more common type and is strongly associated with metabolic syndrome, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
Why is Fatty Liver Dangerous ?
Fatty liver disease becomes dangerous when too much fat builds up in the liver, making it harder for the liver to work properly. The liver plays a key role in digestion, detoxification, and energy storage, so any damage to it can affect the entire body.
If fatty liver is not treated, it can lead to inflammation and liver cell damage. Over time, this can develop into more serious conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, or cirrhosis. These advanced stages may cause permanent liver damage and increase the risk of liver failure or liver cancer.
Many people with early-stage fatty liver disease may not notice any symptoms. This makes it important to take early steps to manage the condition, even if there are no warning signs. Regular health check-ups can help detect fatty liver early.
One of the best ways to protect the liver is by following a healthy fatty liver diet. Eating the right foods helps reduce fat buildup, improve liver function, and prevent further damage.
Key Dietary Principles for Fatty Liver Disease
A liver-friendly diet aims to:
Reduce liver fat and inflammation
Promote weight loss (if overweight)
Improve insulin sensitivity
Lower cholesterol and triglycerides
Support overall metabolic health
Key foods to avoid or limit:
Added sugars (especially fructose and high-fructose corn syrup)
Refined carbohydrates (white bread, pasta, sugary cereals)
Saturated and trans fats (fried foods, processed snacks)
Excessive alcohol
Red and processed meats
Key foods to include:
Fruits and vegetables
Whole grains
Lean proteins
Healthy fats (especially omega-3 fatty acids)
Foods rich in antioxidants and fiber
Top Fatty Liver Diet Plans
Mediterranean Diet

The Mediterranean diet comes from the traditional eating patterns of countries near the Mediterranean Sea. It focuses on fresh, natural foods that support overall health and well-being.
This way of eating includes lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes. It also encourages healthy fats like olive oil and lean proteins such as fish and poultry. Red meat and processed foods are limited.
The Mediterranean diet is often recommended as an ideal fatty liver diet. Its rich mix of nutrients helps reduce fat in the liver, improve heart health, and lower inflammation. Following this diet can be a simple and tasty way to manage fatty liver disease and support long-term liver health.
Why it helps fatty liver
Rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds from fruits, vegetables, nuts, and olive oil
High in monounsaturated fats, particularly from olive oil, which improve liver fat metabolism
Includes omega-3 fatty acids from fish, which reduce liver fat and inflammation
Supports weight loss and improves insulin sensitivity
Key foods
Olive oil, nuts, seeds
Fresh fruits and vegetables
Whole grains like quinoa, barley, and brown rice
Fish and seafood (at least twice a week)
Moderate intake of poultry, eggs, dairy, and legumes
Limited red meat and sweets
Scientific evidence: Studies show that the Mediterranean diet reduces liver fat and improves liver enzyme levels in NAFLD patients.
DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)

The DASH diet was originally created to help lower high blood pressure. Over time, it has also been recognized for its benefits in improving overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
This diet focuses on eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins like chicken or fish, and low-fat dairy products. It also limits foods high in sodium, added sugars, and unhealthy fats.
The DASH diet can also work well as a fatty liver diet. Its balanced meals help reduce fat in the liver, support weight loss, and improve metabolic health. By following this diet, people with fatty liver disease can manage their condition more effectively and improve their liver function.
Why it helps fatty liver
Low in saturated fat and added sugars
High in fiber which aids in reducing fat absorption and improving metabolism
Improves insulin resistance and promotes weight loss
Key foods
Fresh fruits and vegetables
Whole grains
Low-fat dairy products
Lean meats, poultry, and fish
Nuts, seeds, and legumes
Limits on salt, red meat, sweets, and sugary beverages
Plant-Based Diet

A plant-based diet centers on eating mostly or only foods that come from plants. This includes vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. It avoids or limits animal-based foods like meat, dairy, and eggs.
This way of eating provides the body with essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants. It can help reduce inflammation, support weight loss, and lower the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart problems.
A plant-based diet is also a good option for a fatty liver diet. The high fiber and low fat content help reduce fat buildup in the liver. By focusing on healthy plant foods, this diet can improve liver health and support recovery from fatty liver disease.
Why it helps fatty liver
High in fiber which aids liver fat reduction
Rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals that fight inflammation
Low in saturated fat and cholesterol
Helps reduce body weight and improve insulin sensitivity
Key foods
Leafy greens and colorful vegetables
Fresh fruits
Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas
Whole grains like oats, barley, and brown rice
Nuts and seeds (in moderation)
Avoid or limit animal products
Low-Carbohydrate Diet

A low-carbohydrate diet limits the amount of carbs you eat, such as bread, pasta, and sugary foods. This encourages the body to use stored fat for energy instead of relying on carbohydrates.
By lowering carb intake, the body begins to burn fat more effectively. This can lead to weight loss, improved blood sugar levels, and better metabolic health. It may also reduce fat stored in the liver.
A low-carbohydrate diet can be a helpful fatty liver diet. Reducing carbs can lower liver fat, improve insulin resistance, and support liver function. When followed correctly, it may help manage or even reverse early stages of fatty liver disease through healthy eating and weight control.
Why it helps fatty liver
Reduces insulin resistance, which is a key driver of liver fat accumulation
Promotes weight loss, especially loss of visceral fat around the liver
Lowers blood sugar and triglycerides
Key foods
Lean meats, fish, eggs
Non-starchy vegetables (broccoli, spinach, kale)
Healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, and nuts
Limited fruits and whole grains
Avoid refined carbs and sugars
High-Fiber Diet

High-fiber diets focus on consuming foods that are rich in dietary fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. These foods are known for their ability to improve digestion and promote overall gut health.
Fiber helps regulate bowel movements, reduce cholesterol levels, and support a healthy metabolism. It also aids in weight management by keeping you full longer, which can help reduce fat buildup in the body.
A high-fiber diet is beneficial for a fatty liver diet. By improving digestion and metabolism, it helps prevent excess fat from accumulating in the liver. Including fiber-rich foods in your daily meals can support liver health, reduce inflammation, and assist in managing or reversing fatty liver disease.
Why it helps fatty liver
Fiber slows absorption of sugar and fat, reducing liver fat buildup
Supports gut health, which is linked to liver health
Helps with weight management and insulin sensitivity
Key foods
Whole grains (brown rice, oats, quinoa)
Fruits with skin (apples, pears, berries)
Vegetables, especially leafy greens and cruciferous veggies
Legumes and beans
Nuts and seeds
Anti-Inflammatory Diet

An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on consuming foods that reduce inflammation in the body. This includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, especially those rich in omega-3 fatty acids like fish and flaxseeds.
Chronic inflammation is linked to several health problems, including liver diseases. By choosing anti-inflammatory foods, you can help reduce inflammation and support your body’s natural healing processes.
For those with fatty liver disease, an anti-inflammatory diet can be a great addition to a fatty liver diet. It helps reduce liver inflammation, improve liver function, and prevent further damage. This diet supports overall liver health and can help manage or even reverse fatty liver disease when combined with other lifestyle changes.
Why it helps fatty liver
Fatty liver is an inflammatory condition; reducing systemic inflammation helps prevent liver damage
Includes foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids
Key foods
Fatty fish (salmon, sardines)
Berries, cherries, and citrus fruits
Leafy green vegetables
Nuts, seeds, and olive oil
Spices like turmeric and ginger
Avoid processed and fried foods, sugar, and refined carbs
Intermittent Fasting (IF)

Intermittent fasting is a dietary approach that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. One common method is the 16/8 approach, where you fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window.
This pattern helps regulate insulin levels, improves metabolism, and can lead to weight loss. By fasting, the body uses stored fat for energy, which can help reduce fat accumulation, especially in the liver.
Intermittent fasting can be an effective part of a fatty liver diet. It helps lower liver fat, improve liver function, and reduce inflammation. When combined with a balanced diet, intermittent fasting may support the reversal of fatty liver disease and promote overall liver health.
Why it helps fatty liver
Reduces insulin resistance and promotes fat burning
Leads to weight loss and reduced liver fat
Improves metabolic health
Key approach
Time-restricted eating (16:8 or 18:6 schedules)
Avoid overeating during feeding windows
Focus on nutrient-dense, whole foods during eating periods
Low-Fat Diet

A low-fat diet focuses on reducing total fat intake, especially unhealthy fats like saturated and trans fats. This approach encourages the consumption of healthier fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, and fish.
Limiting unhealthy fats helps reduce the risk of heart disease, obesity, and other health problems. It also supports healthy liver function by preventing excess fat from accumulating in the liver.
For those with fatty liver disease, a low-fat diet is beneficial. By cutting back on unhealthy fats, it helps prevent further liver damage, reduces inflammation, and supports weight management. Incorporating a low-fat diet as part of a fatty liver diet can improve liver health and promote recovery from fatty liver disease.
Why it helps fatty liver:
Reduces calorie intake and fat absorption
Improves cholesterol and triglyceride levels
Supports weight loss
Key foods
Fruits and vegetables
Whole grains
Lean proteins like skinless poultry and fish
Avoid fried foods, fatty meats, and processed snacks
Practical Tips for a Fatty Liver Diet
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods
Opt for fresh, whole foods rather than packaged snacks or processed meats. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your meals. These foods are rich in essential nutrients and fiber, which support overall health and liver function. A diet based on whole, unprocessed foods is key for managing fatty liver disease.
Choose healthy fats
Instead of using butter or margarine, choose healthier fats like olive oil or avocado oil for cooking. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are also great options due to their omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce liver inflammation. Incorporating these healthy fats into your fatty liver diet can help reduce liver fat and improve function.
Limit Added sugars
Be mindful of hidden sugars in processed foods. Avoid sugary drinks, candies, and desserts that can contribute to liver fat buildup. Instead, focus on natural sugars from whole fruits. Reducing sugar intake is an important step in managing fatty liver disease and preventing further liver damage.
Watch portion sizes
Controlling portion sizes is essential for weight management, which can significantly improve fatty liver. Using smaller plates and paying attention to portion control can help prevent overeating. Losing excess weight can help reduce fat accumulation in the liver, making portion control an important part of a healthy fatty liver diet.
Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water is vital for liver health. Water helps your liver flush out toxins and aids in digestion. Staying hydrated also supports metabolic functions and can improve overall energy levels, which is important when managing fatty liver disease.
Regular meals
Eating regular, balanced meals throughout the day helps keep blood sugar levels stable and prevents overeating. Skipping meals or eating too much at once can increase liver fat buildup. Consistency in meal timing and portion sizes is essential for supporting liver function and managing fatty liver disease effectively.
Sample Daily Meal Plan for Fatty Liver
| Meal | Food |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal topped with fresh berries and a handful of walnuts |
| Green tea or black coffee | |
| Lunch | Grilled salmon salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, avocado, and olive oil dressing |
| Whole grain bread slice | |
| Snack | Apple slices with almond butter |
| Dinner | Quinoa bowl with roasted vegetables, chickpeas, and a lemon-tahini dressing |
| Steamed broccoli | |
| Drink | Plenty of water throughout the day |
Conclusion
In conclusion, a fatty liver diet plays a pivotal role in managing and even reversing fatty liver disease. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, individuals can reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall liver health.
Diets like the Mediterranean, DASH, and plant-based plans, along with approaches like intermittent fasting and low-carb options, have shown significant benefits in reducing inflammation and liver fat. Coupled with regular exercise, portion control, and mindful eating habits, these dietary changes can lead to long-term improvements in liver function and metabolic health. Adopting a fatty liver diet is a powerful, natural way to protect your liver and enhance your well-being, ultimately helping you live a healthier life.
FAQs
Q.1 What is a fatty liver diet ?
A fatty liver diet focuses on eating foods that reduce fat buildup in the liver, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It also limits unhealthy fats, sugars, and processed foods.
Q.2 Can I eat fruits on a fatty liver diet ?
Yes, fruits are an essential part of a fatty liver diet. They provide important vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber that support liver health. Opt for fresh fruits and avoid those with high sugar content.
Q.3 Is it okay to eat fatty foods on a fatty liver diet ?
While healthy fats, such as those from olive oil, avocado, and fatty fish, are beneficial for liver health, saturated and trans fats should be limited. Focus on unsaturated fats to reduce liver fat and inflammation.
Q.4 How can portion control help with fatty liver disease ?
Portion control helps with weight management, which is crucial for reducing fat in the liver. By eating smaller, balanced meals throughout the day, you can help lower liver fat and prevent further liver damage.
Q.5 Is drinking water important for a fatty liver diet ?
Yes, staying hydrated is essential. Water helps flush out toxins from the liver, supports digestion, and aids in overall metabolic health. Drinking enough water each day can support liver function and help with fat reduction.


