Fatty Liver Disease, medically known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver, impairing its function. This vital organ plays a crucial role in detoxifying the body, processing nutrients, and regulating metabolism. When the liver is overwhelmed with fat, it can lead to inflammation, scarring, and even serious liver complications if left unmanaged.
A structured fatty liver diet plan is essential in managing and reversing this condition. This plan typically emphasizes whole foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, lean proteins, and antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables. Cutting down on refined sugars, trans fats, and alcohol is critical to reduce liver strain and promote healing.
Adopting a fatty liver diet plan not only helps reduce liver fat but also supports weight loss, improves insulin sensitivity, and lowers cholesterol. Combined with regular physical activity, this approach can restore liver health and overall well-being over time.
How Does Fatty Liver Form ?
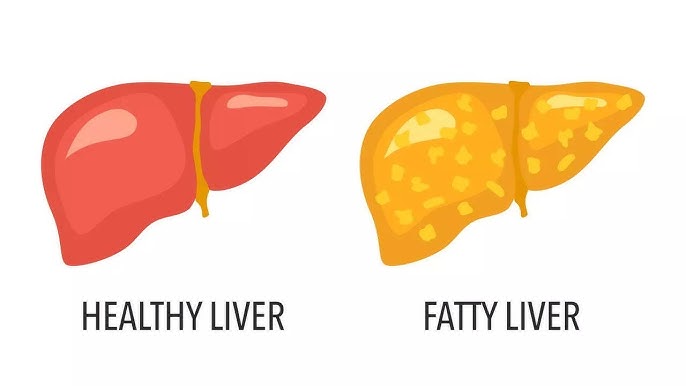
Fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, develops when excess fat accumulates in liver cells. Normally, the liver stores a small amount of fat, but when fat makes up more than 5–10% of the liver’s weight, it’s considered a fatty liver. This condition is often silent in the early stages, showing few or no symptoms. However, over time, it can progress to inflammation (steatohepatitis), scarring (fibrosis), or even cirrhosis.
One of the main causes is poor dietary habits—particularly diets high in sugar, refined carbs, and unhealthy fats. These lead to insulin resistance and elevated triglycerides, which promote fat storage in the liver. Alcohol consumption is another major factor in alcoholic fatty liver disease, while non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is closely tied to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
A sedentary lifestyle also contributes to the development of fatty liver. Lack of physical activity leads to weight gain and worsens insulin resistance.
The good news is that with the right fatty liver diet plan, including whole foods, lean protein, and healthy fats, you can reverse the condition and support liver recovery naturally.
Fatty liver develops when the liver can’t efficiently process fats, leading to fat accumulation in liver cells. It commonly arises due to:
Obesity
Type 2 diabetes
High cholesterol or triglyceride levels
Poor dietary choices
Excessive alcohol intake
There are two main types:
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) – caused by heavy drinking.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) – more common and not related to alcohol.
What Triggers Fatty Liver ?
Fatty liver disease is triggered by various lifestyle and metabolic factors that lead to fat accumulation in liver cells. One of the primary triggers is excessive calorie consumption—especially from refined carbohydrates, sugary beverages, and saturated fats. When the body receives more calories than it can burn, it stores the excess as fat, including in the liver.
Another major contributor is insulin resistance, often seen in individuals with type 2 diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome. When cells stop responding properly to insulin, blood sugar levels rise, prompting the liver to convert glucose into fat. Over time, this process leads to fatty liver development, even in people who don’t consume alcohol.
Certain medications, genetic factors, and rapid weight loss can also trigger fatty liver. Additionally, chronic alcohol use is a leading cause of alcoholic fatty liver disease, which may progress to cirrhosis if left untreated.
The best defense is a healthy lifestyle, and a structured fatty liver diet plan is essential. Focusing on whole foods, limiting added sugars, and incorporating fiber-rich vegetables and lean proteins can help reduce liver fat and restore liver function naturally.
Fatty liver is mostly a lifestyle-induced condition. It often stems from:
Sedentary lifestyle
High-sugar, high-fat diets
Frequent intake of processed foods
Insulin resistance
Why Is It Dangerous ?
If left unmanaged, fatty liver can progress to:
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Liver fibrosis
Cirrhosis
Liver cancer
Early intervention through diet and lifestyle can reverse fatty liver completely in many cases.
When Should You Be Concerned ?
Many people with fatty liver experience no symptoms initially. However, you should consult a doctor if you notice:
Persistent fatigue
Abdominal discomfort
Unexplained weight gain
Elevated liver enzymes on blood tests
How Can Diet Help ?
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing and reversing fatty liver. The right diet can:
Reduce liver inflammation
Promote fat metabolism
Improve insulin sensitivity
Support overall liver health
Now, let’s dive into the Top 8 Diet Tips that are essential for managing fatty liver disease effectively.
🥗 Top 8 Fatty Liver Diet Tips
Embrace a Mediterranean Diet
Embracing a Mediterranean diet is one of the most effective strategies for managing fatty liver disease. This heart-healthy eating style emphasizes whole foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats such as olive oil and nuts. These nutrient-dense foods help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress on the liver.
Incorporating the Mediterranean approach into a fatty liver diet plan means cutting out processed foods, added sugars, and refined carbs, all of which contribute to fat accumulation in the liver. Instead, meals are built around fiber-rich plant foods and lean proteins like fish and chicken, which support better digestion and liver detoxification.
The fatty liver diet plan based on Mediterranean principles has been shown to improve liver enzyme levels and decrease liver fat. When combined with regular exercise and weight management, this diet can lead to long-term improvements in liver health and overall metabolic function.
What to Eat:
Olive oil
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
Nuts (almonds, walnuts)
Whole grains
Fresh fruits and vegetables
Why It Works: The Mediterranean diet is rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and fiber. It reduces liver fat, lowers inflammation, and improves insulin sensitivity.
Benefits:
Improves liver enzyme levels
Reduces risk of heart disease and diabetes
Supports weight loss
Increase Fiber Intake
Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, apples, and beans, binds with cholesterol and helps flush it from the body. This can reduce liver fat and improve overall liver function. Insoluble fiber, present in vegetables and whole grains, supports healthy digestion and prevents constipation, which indirectly benefits liver health.

A well-structured fatty liver diet plan that includes high-fiber foods not only promotes better liver health but also supports heart health and stable blood sugar levels. Gradually increasing daily fiber intake while staying hydrated can make a noticeable difference in liver enzyme levels over time.
What to Eat:
Oats, barley
Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, black beans)
Vegetables (broccoli, spinach)
Fruits (apples, berries, pears)
Why It Works: Fiber slows down digestion, regulates blood sugar, and helps eliminate toxins and fat from the liver.
Benefits:
Promotes satiety and aids weight loss
Reduces cholesterol
Enhances gut health
Avoid Added Sugars and Fructose
Avoiding added sugars and fructose is essential when following a fatty liver diet plan. These sugars, commonly found in soft drinks, sweets, baked goods, and processed foods, contribute significantly to fat buildup in the liver. Fructose, in particular, is metabolized in the liver and can easily be converted into fat, worsening hepatic steatosis.
By eliminating sugary foods and beverages, individuals can reduce liver inflammation and support fat reduction in liver cells. A well-designed fatty liver diet plan focuses on natural sources of sweetness, such as whole fruits, which contain fiber and nutrients that help counteract the effects of fructose. Reading nutrition labels and avoiding high-fructose corn syrup is also a smart step.
Incorporating low-glycemic, whole foods instead of processed sugar helps stabilize blood sugar and insulin levels, both of which are crucial for reversing fatty liver. Long-term commitment to a sugar-free fatty liver diet plan supports lasting liver health and metabolic balance.
What to Avoid:
Sugary drinks (soda, sweetened juices)
Pastries, cakes, cookies
Candy and ice cream
Processed foods with corn syrup
Why It Works: Fructose is directly converted into fat by the liver. Reducing sugar intake immediately reduces liver fat levels.
Benefits:
Decreases triglycerides
Reduces insulin resistance
Slows fatty liver progression
Choose Lean Protein Over Red Meat
Choosing lean protein over red meat is a key element of a successful fatty liver diet plan. Red meats like beef, pork, and lamb are high in saturated fats, which can contribute to liver inflammation and fat accumulation. In contrast, lean proteins such as chicken breast, turkey, tofu, fish, and legumes provide essential amino acids without the harmful fats that strain the liver.
Incorporating these healthier protein sources supports muscle maintenance while easing the liver’s workload. For example, grilled chicken, steamed fish, and lentil soups are excellent choices for meals in a fatty liver diet plan. These options are not only lower in fat but also rich in nutrients like omega-3s and antioxidants.
Making small shifts—like replacing ground beef with ground turkey or choosing plant-based proteins a few times a week—can make a big difference. A balanced fatty liver diet plan that emphasizes lean protein helps reduce fat in the liver and promotes long-term liver health.
What to Eat:
Skinless chicken breast
Fish and seafood
Plant-based proteins (tofu, tempeh)
Eggs (especially egg whites)
Why It Works: Red meat is often high in saturated fat. Lean protein helps build muscle, burn more fat, and reduces liver stress.
Benefits:
Improves body composition
Reduces inflammation
Promotes liver repair
Limit Refined Carbohydrates
Limiting refined carbohydrates is a crucial component of an effective fatty liver diet plan. Foods like white bread, pasta, pastries, and sugary cereals can spike blood sugar levels and promote fat accumulation in the liver. These “empty carbs” offer little nutritional value and can worsen insulin resistance, a common contributor to fatty liver disease.

Instead, focus on whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley. These complex carbs are digested more slowly, providing sustained energy without overwhelming your liver. Including more fiber-rich vegetables and legumes also supports digestive health and reduces liver fat.
By reducing your intake of refined carbs and choosing nutrient-dense alternatives, you help stabilize blood sugar, lower inflammation, and ease the burden on your liver. This small but powerful change in your fatty liver diet plan can greatly improve liver function and support overall health in the long run.
What to Avoid:
White rice, white bread
Pasta made with white flour
Baked goods made from refined flour
What to Eat Instead:
Brown rice
Quinoa
Whole wheat bread
Sweet potatoes
Why It Works: Refined carbs spike insulin levels and contribute to fat accumulation in the liver.
Benefits:
Stabilizes blood sugar
Lowers fat buildup in liver
Aids in weight loss
Include Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Including antioxidant-rich foods is essential in any effective fatty liver diet plan. Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, which can damage liver cells and worsen fatty liver disease. Vitamins C and E, selenium, and polyphenols found in plant-based foods are especially helpful in protecting and repairing liver tissue.
Foods such as berries, citrus fruits, spinach, kale, nuts, green tea, and turmeric are excellent sources of natural antioxidants. These nutrient-dense options not only reduce inflammation but also support the liver’s natural detoxification processes. Regularly consuming these foods can slow disease progression and improve liver enzyme levels.
Making antioxidant-rich foods a regular part of your fatty liver diet plan helps restore liver health over time. Alongside limiting unhealthy fats, sugars, and processed foods, this approach provides the nutritional support your body needs to heal. It’s a powerful, natural step toward better liver function and overall wellness.
What to Eat:
Green tea
Berries (blueberries, strawberries)
Leafy greens (kale, collard greens)
Turmeric, garlic, ginger
Why It Works:
Antioxidants neutralize harmful free radicals that damage liver cells and contribute to inflammation.
Benefits:
Supports liver detoxification
Slows liver scarring
Enhances immune function
Stay Hydrated and Cut Out Alcohol
Staying hydrated and avoiding alcohol are critical components of an effective fatty liver diet plan. Water helps flush out toxins and supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes. Proper hydration also aids digestion and promotes metabolic function, making it easier for your liver to break down fat.
Alcohol, on the other hand, is a major contributor to liver damage. Even small amounts can worsen inflammation and fat buildup in the liver. If you’re dealing with fatty liver disease, cutting out alcohol completely is one of the most important lifestyle changes you can make. It gives your liver a chance to heal and regenerate.
As part of your fatty liver diet plan, aim to drink at least 8–10 glasses of water daily and replace alcoholic beverages with healthier alternatives like herbal teas, infused water, or sparkling water with lemon. This simple shift can significantly improve liver function and overall well-being.
What to Drink:
Water
Herbal teas (dandelion, milk thistle, green tea)
Lemon water
What to Avoid:
Alcohol (even in small amounts)
Energy drinks
Sweetened coffee beverages
Why It Works:
Proper hydration supports digestion and liver detox. Alcohol directly harms liver cells and worsens fatty liver.
Benefits:
Enhances metabolic processes
Flushes out toxins
Prevents further liver damage
Practice Intermittent Fasting or Controlled Portions
Practicing intermittent fasting or eating controlled portions can significantly support a fatty liver diet plan. Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting, which can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce liver fat. It gives your body time to burn through stored glucose and tap into fat reserves, including the fat stored in your liver.

If intermittent fasting isn’t suitable for your lifestyle, focusing on portion control is just as effective. Overeating—even healthy foods—can still contribute to fat buildup in the liver. Using smaller plates, avoiding second helpings, and listening to hunger cues are simple yet powerful ways to manage intake.
Incorporating intermittent fasting or portion control into your fatty liver diet plan can lead to gradual, sustainable weight loss, which is essential for improving liver health. These strategies, paired with a balanced diet and regular exercise, help reduce liver inflammation and promote better long-term outcomes.
How to Do It:
16:8 method (16 hours fast, 8-hour eating window)
Eat small, balanced meals
Avoid late-night eating
Why It Works: Fasting allows your liver time to process fat without constant insulin spikes. Caloric control promotes fat burning.
Benefits:
Helps with weight reduction
Enhances fat metabolism
Improves insulin response
✅ Bonus: Foods That Help Reverse Fatty Liver
Avocados – full of healthy fats and fiber
Coffee (in moderation) – may reduce liver enzyme levels
Beets – rich in betalains, which aid detox
Nuts – protect against NAFLD progression
Tofu – low in fat and high in protein
🍽️ Sample One-Day Fatty Liver Meal Plan
Here is your meal plan in table format with the keyword fatty liver diet plan included:
| Meal | Menu |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | 1 bowl of oatmeal with blueberries and chia seedsGreen tea |
| Mid-Morning Snack | A handful of walnuts or almonds |
| Lunch | Grilled salmon with quinoa salad and olive oil dressingSteamed broccoli |
| Evening Snack | Apple slices with 1 tbsp almond butter |
| Dinner | Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetablesBrown rice or whole grain rotiHerbal tea (milk thistle or dandelion) |
This fatty liver diet plan focuses on whole foods, healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants to support liver health and reduce fat buildup.
🧘 Lifestyle Tips to Complement the Diet
Exercise at least 30 minutes daily (walking, yoga, cycling)
Manage stress through meditation or mindfulness
Get 7–8 hours of quality sleep
Avoid smoking and excessive medications
Regularly monitor liver enzymes with your doctor
📚 Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is both preventable and reversible with the right dietary and lifestyle adjustments. By recognizing its root causes and adopting a strategic, nutrient-dense approach, you can significantly reduce fat accumulation in the liver and promote its healing. A well-balanced fatty liver diet plan plays a central role in this transformation.

The 8 dietary strategies discussed above—like increasing fiber, cutting added sugars, and choosing lean proteins—are designed to reduce inflammation and support liver regeneration. Consistency and moderation are vital. You don’t need perfection; you need a plan that’s sustainable and rich in whole, liver-friendly foods.
Your liver works tirelessly to detoxify your body and regulate metabolism. It’s time to return the favor with mindful choices. Start implementing a fatty liver diet plan today, and take the first step toward renewed liver function, improved energy, and long-term health. A cleaner diet can truly mean a cleaner, healthier you.
FAQs
Q1. What is the best fatty liver diet plan to reverse the condition ?
The best fatty liver diet plan focuses on whole, unprocessed foods rich in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats. A Mediterranean-style approach—emphasizing vegetables, fruits, legumes, fish, olive oil, and whole grains—has been proven effective. Limiting added sugars, red meat, and refined carbs also helps reduce liver fat and inflammation.
Q2. Can a fatty liver diet plan include carbohydrates ?
Yes, but the type of carbohydrates matters. A good fatty liver diet plan includes complex carbs like oats, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and brown rice instead of refined sugars and white flour products. These complex carbs are rich in fiber, which supports digestion and helps control blood sugar levels—both important for liver health.
Q3. Is intermittent fasting safe for fatty liver ?
Intermittent fasting can complement a fatty liver diet plan when done properly. Time-restricted eating helps regulate insulin, reduce inflammation, and improve fat metabolism. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting, especially if you have diabetes or other medical conditions.
Q4. How long does it take to see results from a fatty liver diet plan ?
Improvements can begin in as little as 2–3 weeks, but noticeable changes in liver function may take a few months. Following a fatty liver diet plan consistently, alongside regular exercise and hydration, can significantly reduce liver fat and inflammation over time.
Q5. Can I eat fats on a fatty liver diet plan ?
Yes, but focus on healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish. These support heart and liver health. A proper fatty liver diet plan limits saturated and trans fats (from fried foods, processed snacks, and red meat), which can worsen liver damage.