Athletes constantly aim to boost performance, speed up recovery, and stay in top physical shape. One of the most important tools to reach these goals is proper nutrition. It’s not only about eating enough food but also about choosing the right types of nutrients that support energy, endurance, and muscle health.
A healthy diet for athletes must be well-balanced and timed correctly. This means combining carbohydrates for energy, proteins for muscle repair, and healthy fats for overall wellness. Hydration and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals also play a key role in keeping the body functioning at its best. Eating the right foods before and after training helps athletes get the most out of every workout and recover faster.
Whether you’re a professional athlete or someone who enjoys regular workouts, understanding what your body needs can make a big difference. In this article, we’ll break down the essentials of a healthy diet for athletes and show you how to fuel your body the right way.
The Role of Nutrition in Athletic Performance

Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting athletic performance and recovery. Proper nutrition helps:
Energy Levels: Athletes need a high amount of energy to perform well during training, competitions, and daily routines. A healthy diet for athletes includes the right mix of carbohydrates, healthy fats, and proteins, which are the body’s main fuel sources. These nutrients help maintain stamina, improve endurance, and keep the body energized throughout the day.
Muscle Repair and Growth: Protein is especially important for athletes, as it helps repair and rebuild muscle tissue after intense workouts. A healthy diet for athletes should include enough protein to support muscle recovery and growth, helping them gain strength and reduce the risk of injury.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance: Staying well-hydrated is vital for athletes. Water and electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium help maintain fluid balance, prevent muscle cramps, and support proper muscle function. A healthy diet for athletes should ensure both hydration and adequate electrolyte intake.
Immune Function: Hard training can sometimes lower the immune system. A healthy diet for athletes should provide enough vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to strengthen the immune system and help the body fight off illness.
Recovery: What athletes eat after exercising plays a big role in how fast and well they recover. A healthy diet for athletes should focus on restoring energy levels, repairing muscle tissue, and reducing inflammation, all of which support better overall recovery and long-term performance.
Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of an Athlete’s Diet
Athletes need to focus on the three main macronutrients: carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Each plays a unique and essential role in fueling the body for training and competition.
Carbohydrates: The Primary Energy Source

Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy, especially during intense physical activity. When athletes train or compete, their bodies rely heavily on carbohydrates to maintain stamina and performance. These carbohydrates are stored as glycogen in the muscles and liver and are later converted into glucose to fuel the body during exercise.
Including enough carbohydrates in a healthy diet for athletes is essential for keeping energy levels high and preventing fatigue. Without adequate carbs, performance may decline, and recovery can take longer. For athletes, eating the right amount of carbohydrates ensures their bodies are always ready for physical demands.
Complex Carbohydrates: These include whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. They are digested slowly, providing a steady and sustained release of energy.
Simple Carbohydrates: These include fruits and dairy. They are broken down quickly, offering a rapid source of energy.
Carbohydrate needs for athletes vary based on their sport, training intensity, and duration. For example:
Endurance athletes (e.g., long-distance runners, cyclists) typically need a higher carbohydrate intake to maintain glycogen stores.
Strength athletes (e.g., weightlifters) may focus more on protein and fat but still require adequate carbs for overall energy.
Protein: The Key to Muscle Repair and Growth
Protein plays a key role in repairing, maintaining, and building muscles. During intense training or workouts, muscle fibers experience small tears. To recover and grow stronger, the body needs enough protein to rebuild these damaged fibers effectively.
Including sufficient protein in a healthy diet for athletes is important for long-term strength and performance. It not only helps muscles recover faster but also supports endurance and reduces the risk of injury. Athletes who follow a well-balanced plan with the right protein intake can maintain lean muscle mass and continue improving their physical abilities over time.
Complete Proteins: Found in animal products (chicken, beef, fish, eggs, and dairy), complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
Incomplete Proteins: Found in plant-based foods (beans, nuts, seeds, and grains), incomplete proteins lack one or more essential amino acids. However, combining different plant-based foods can provide a complete amino acid profile.
The general protein recommendation for athletes is between 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, depending on the type and intensity of the activity.
Fats: Essential for Long-Term Energy and Hormonal Health

Fats are an important energy source, especially during low-intensity or long-duration activities like endurance training. While carbohydrates fuel high-intensity efforts, fats help sustain energy when the body is working over a longer period. This makes them a vital part of an athlete’s fuel system.
In addition to providing energy, fats support vital functions such as cell health, brain performance, and hormone production. Some of these hormones are involved in muscle growth and recovery. Including healthy fats in a healthy diet for athletes ensures better overall performance, faster recovery, and long-term physical and mental well-being.
Healthy Fats: Sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon. These fats contain essential fatty acids such as omega-3s, which help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
Saturated Fats and Trans Fats: While these fats are needed in small amounts, excessive consumption of saturated fats (found in red meat and full-fat dairy) and trans fats (found in processed foods) can contribute to chronic health issues, such as cardiovascular disease.
Athletes should aim to get about 20-35% of their daily caloric intake from fats, with a focus on healthy sources.
Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals for Optimal Performance
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) are also essential for an athlete’s overall health and performance. While they are required in smaller amounts, their roles are vital.
Vitamins
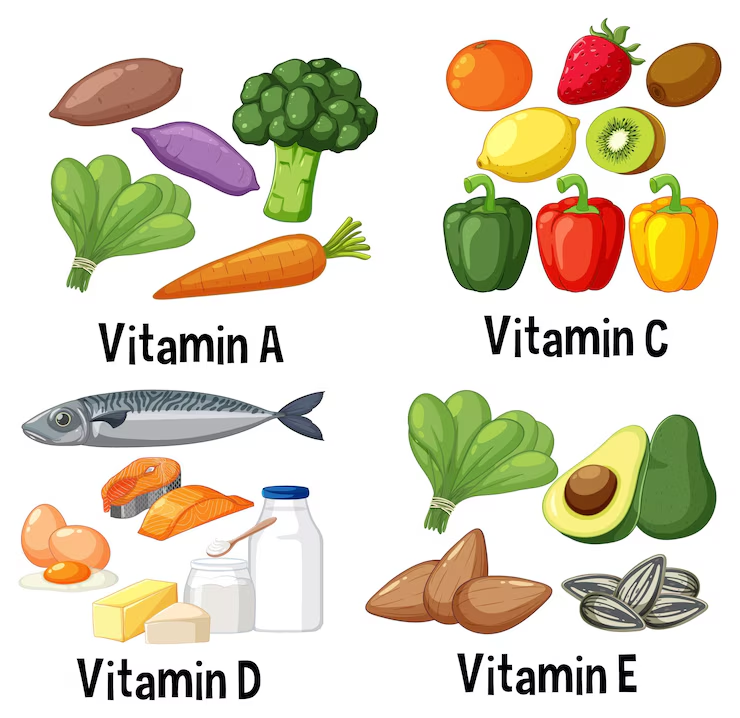
Vitamin C: This powerful antioxidant helps reduce inflammation and boosts the immune system, both of which are important for active individuals. A healthy diet for athletes should include vitamin C-rich foods such as oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers to support recovery and protect against illness.
Vitamin D: Essential for strong bones and a well-functioning immune system, vitamin D also supports muscle health. It is made in the body through sunlight exposure and can be obtained from foods like fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and fatty fish. A healthy diet for athletes should ensure enough vitamin D for overall strength and resilience.
B Vitamins: These vitamins help convert food into usable energy, making them vital for endurance and performance. Athletes often need more B vitamins, particularly B12 and B6. B12 is found in animal-based foods, while B6 is present in poultry, fish, and whole grains. Including these nutrients in a healthy diet for athletes helps maintain energy levels and reduce fatigue.
Minerals
Calcium: Calcium is vital for strong bones and proper muscle function, both of which are important for athletic performance. A healthy diet for athletes should include sources like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milks to support bone strength and reduce injury risk.
Iron: Iron plays a key role in carrying oxygen through the blood, helping athletes maintain energy and endurance. A healthy diet for athletes should include iron-rich foods such as red meat, poultry, beans, and spinach to support stamina and reduce fatigue.
Magnesium: This mineral supports muscle function, helps prevent cramps, and aids in muscle relaxation after workouts. A healthy diet for athletes should include magnesium-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and leafy greens to support recovery and overall performance.
Potassium: Potassium helps keep fluid levels balanced and prevents muscle cramps during intense exercise. A healthy diet for athletes should include foods like bananas, potatoes, and tomatoes to maintain hydration and muscle health.
Athletes should aim to get a variety of vitamins and minerals through a well-rounded diet, ensuring they meet the increased demands that come with physical activity.
Hydration: The Cornerstone of Athletic Performance
Proper hydration is key to maintaining optimal performance during exercise. Even mild dehydration can lead to fatigue, reduced endurance, and impaired decision-making. Dehydration can also hinder muscle function and increase the risk of injury.
Hydration Strategies

Pre-Exercise: Staying hydrated before exercise is important for maintaining energy and performance. Throughout the day, athletes should drink plenty of water to stay prepared for training. About 2–3 hours before a workout, it’s recommended to drink 16–20 ounces of water. Then, drink another 8–10 ounces around 20–30 minutes before starting. A healthy diet for athletes should always include proper hydration to support performance and prevent early fatigue.
During Exercise: While exercising, especially during long or high-intensity sessions, it’s important to keep sipping water regularly. Athletes should aim to drink 7–10 ounces every 10–20 minutes. If the workout lasts more than an hour, sports drinks with added electrolytes like sodium and potassium can help maintain balance and energy. This practice is an important part of a healthy diet for athletes to stay fueled and hydrated.
Post-Exercise: After finishing a workout, rehydration is just as crucial as the training itself. Athletes should replace fluids lost through sweat by drinking 16–24 ounces of water for every pound of body weight lost. Including water, electrolyte-rich drinks, and nutrient-dense foods in a healthy diet for athletes helps speed up recovery, restore balance, and prepare the body for the next session.
Nutrition Timing: When to Eat for Optimal Performance
What you eat and when you eat can make a significant difference in your athletic performance. Nutrition timing involves eating the right nutrients before, during, and after exercise to optimize energy levels, enhance performance, and accelerate recovery.
Pre-Workout Nutrition
Fueling your body before a workout is essential to give you the energy and strength needed for top performance. Eating a balanced meal or snack that includes both carbohydrates for energy and a small amount of protein for muscle support can make a big difference. Try to eat this meal 30 minutes to 2 hours before your exercise session. Including this routine as part of a healthy diet for athletes helps improve endurance, reduce fatigue, and support better workout results.
Ideal Pre-Workout Foods: A banana with almond butter, a small bowl of oatmeal with berries, or a whole-grain toast with turkey.
Post-Workout Nutrition
After exercise, your muscles need to recover, repair, and restore their glycogen levels. To support this process, it’s important to eat a mix of carbohydrates and protein within 30 to 60 minutes after finishing your workout. This helps refuel energy stores and promotes muscle healing. Including this habit in a healthy diet for athletes is key to faster recovery, reduced soreness, and better performance in future workouts.
Ideal Post-Workout Foods: A protein shake with fruit, chicken with sweet potatoes, or a whole-grain wrap with lean protein and vegetables.
Supplements: Do Athletes Need Them ?
While a well-balanced diet is the best way to get essential nutrients, some athletes might benefit from certain supplements to enhance their performance and recovery. These supplements can help fill in nutritional gaps when needed. However, they should only be used to support—not replace—a healthy diet for athletes.

Protein Powders: Whey or plant-based protein powders can be a convenient way to meet daily protein needs, especially for athletes with high training demands. Including protein supplements as part of a healthy diet for athletes can support muscle repair and growth when whole food options are limited.
Creatine: Commonly used by strength and power athletes, creatine can help increase power, improve performance during high-intensity workouts, and support faster muscle recovery. It can be a useful addition to a healthy diet for athletes focused on strength and endurance.
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): BCAAs may help reduce muscle soreness and support quicker recovery after intense training. Adding them to a healthy diet for athletes can be especially beneficial during periods of heavy exercise or muscle strain.
Multivitamins: If an athlete’s diet is restricted or lacks variety, multivitamins can help fill in nutritional gaps. When used correctly, they can complement a healthy diet for athletes and support overall health and performance.
Conclusion: A Effective Approach to Diet for Athletes

In conclusion, a healthy diet for athletes is essential for maximizing performance, enhancing recovery, and maintaining overall health. Proper nutrition, including the right balance of carbohydrates, protein, fats, and micronutrients, fuels the body for training and competition, while also supporting muscle growth and recovery. Hydration plays a key role in sustaining energy levels and preventing injury, and nutrition timing ensures that athletes can optimize their performance both before and after exercise.
By adopting a tailored, nutrient-dense approach to their diet, athletes can achieve their fitness goals more effectively. Ultimately, a healthy diet for athletes is not just about fueling the body, but also about making informed dietary choices that promote long-term health and well-being. With the right guidance and dedication to nutrition, athletes can unlock their full potential and perform at their best.


