Inflammation is a natural and vital process in the body, helping the immune system protect against injury, infection, and harmful substances. This response is essential for healing and recovery. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can quietly harm tissues and organs, leading to serious health issues like heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and some cancers.
The good news is that what you eat plays a significant role in controlling inflammation. The Anti-Inflammatory Diet focuses on consuming nutrient-rich foods that help reduce chronic inflammation and support overall health. By making smart food choices, you can calm the immune system and promote healing naturally.
Adopting the Anti-Inflammatory Diet is a powerful way to lower inflammation, protect your body from long-term damage, and boost your wellbeing. This natural approach not only improves your health but also enhances your quality of life through mindful eating habits.
Understanding Inflammation: Friend and Foe

Inflammation is your body’s natural response to injury or infection. When you get a cut or hurt yourself, you might notice redness, swelling, and warmth around the affected area. This reaction, called acute inflammation, is an essential part of the healing process, helping to protect the body and start tissue repair.
While acute inflammation is beneficial, chronic inflammation can be harmful if it persists over time. It may silently damage your body and contribute to serious health problems. That’s why managing inflammation is so important for long-term health and wellness.
One effective way to control chronic inflammation is through the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. This diet emphasizes eating nutrient-rich, whole foods that help reduce inflammation naturally, support the immune system, and promote overall well being. Adopting the Anti-Inflammatory Diet can improve your health and protect your body from inflammation-related diseases.
Chronic inflammation, however, is quite different. It is a low-grade, persistent condition that can quietly damage your tissues over time. This ongoing inflammation is associated with numerous modern chronic diseases, posing serious health risks.
Cardiovascular disease
Type 2 diabetes
Alzheimer’s disease
Arthritis
Autoimmune conditions
Certain cancers
What Causes Chronic Inflammation ?
Several lifestyle factors contribute, including:
Poor diet (high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats)
Sedentary lifestyle
Stress
Smoking
Environmental toxins
The foods you consume are a major player in either triggering or calming inflammation.
What Is the Anti-Inflammatory Diet ?

The Anti-Inflammatory Diet isn’t about following strict rules or cutting out entire food groups. Instead, it focuses on making balanced, mindful choices that support your body’s natural ability to fight inflammation. This approach encourages you to enjoy a wide range of whole, nutrient-rich foods—such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins—that nourish the body and help reduce chronic inflammation.
By regularly including these wholesome foods, the Anti-Inflammatory Diet delivers essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. These nutrients play a key role in calming the immune system, supporting digestive health, and protecting the body from damage caused by long-term inflammation. This not only helps reduce symptoms like pain and fatigue but also strengthens your body’s defense against chronic diseases.
Adopting the Anti-Inflammatory Diet can be a sustainable and enjoyable lifestyle change. It’s not about restriction but about making healthier, informed food choices that promote healing and long-term wellbeing. With variety, flexibility, and delicious options, the Anti-Inflammatory Diet can help you feel better, reduce health risks, and support overall wellness naturally.
This diet emphasizes
Fresh fruits and vegetables
Healthy fats (like omega-3 fatty acids)
Whole grains
Lean protein sources
Herbs and spices with antioxidant properties
It discourages:
Processed and fried foods
Excessive sugar
Refined carbohydrates
Trans fats and saturated fats from unhealthy sources
Excessive alcohol
Origins and Research
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet is inspired by traditional eating patterns like the Mediterranean diet and the DASH diet. These diets are well-known for their ability to lower inflammation and reduce the risk of chronic diseases, making them a foundation for the Anti-Inflammatory Diet approach.
Research shows that people who follow these diets often have lower levels of inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These markers indicate the presence of inflammation in the body, so reducing them can help protect overall health.
By adopting the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, you can benefit from these proven effects. This diet encourages nutrient-rich, whole foods that help decrease inflammation, supporting long-term health and reducing the risk of inflammation-related diseases.
Key Components of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Let’s break down the major elements of this diet.
Colorful Fruits and Vegetables

Fruits and vegetables are an important part of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. They are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and natural compounds that help reduce inflammation in the body. These nutrients support the immune system and help cells function properly.
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet works by lowering oxidative stress. This happens when fruits and vegetables neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage tissues and increase inflammation. By eating more of these foods, the body stays protected against chronic diseases linked to inflammation.
Adding a mix of colorful fruits and vegetables to your meals is a simple way to stay healthy. Berries, leafy greens, bell peppers, and sweet potatoes are great examples. These foods not only follow the Anti-Inflammatory Diet but also improve your overall health, energy, and well-being. Including them every day can make a big difference over time.
Best picks
Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
Leafy greens (spinach, kale, Swiss chard)
Cruciferous veggies (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts)
Tomatoes
Bell peppers
Carrots
Healthy Fats
Not all fats are harmful—some are essential for good health. In the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, healthy fats play a key role in reducing inflammation and supporting the body’s natural functions. These fats help protect cell structure and promote overall balance in the body.
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet includes good fat sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish such as salmon. These foods are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and other helpful compounds that lower inflammation and support brain and heart health.
Adding these healthy fats to your daily meals not only improves taste but also strengthens your body’s ability to fight chronic inflammation. By making wise fat choices, the Anti-Inflammatory Diet becomes an easy and natural way to protect your health and maintain long-term wellness.
Best sources
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) rich in omega-3 fatty acids
Olive oil (extra virgin)
Avocados
Nuts (walnuts, almonds)
Seeds (chia, flaxseeds)
Whole Grains

Whole grains are a valuable component of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, offering fiber and essential nutrients that help keep the body balanced and blood sugar levels stable. Unlike refined grains, whole grains retain their bran and germ, providing more health benefits.
The fiber found in whole grains supports healthy digestion and promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. A well-balanced gut environment is closely linked to reduced inflammation, making whole grains an effective way to lower the risk of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Adding whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat to your meals is a simple yet impactful way to follow the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. These nutrient-rich options not only help manage inflammation naturally but also support overall wellness and sustained energy throughout the day.
Best choices
Brown rice
Quinoa
Oats
Barley
Whole wheat
Lean Proteins
Protein is a key element of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, playing an essential role in tissue repair, muscle maintenance, and immune support. It helps the body recover, stay resilient, and function optimally—especially important when dealing with inflammation.
To truly benefit from protein, it’s important to choose clean, lean sources. The Anti-Inflammatory Diet emphasizes options like skinless poultry, fatty fish rich in omega-3s, plant-based proteins such as beans and legumes, and minimally processed tofu. These sources provide nutrients without added fats or chemicals that could worsen inflammation.
Including these healthy proteins in the Anti-Inflammatory Diet supports the body’s natural healing and helps reduce chronic inflammation over time. Regularly consuming lean protein also contributes to balanced nutrition and overall wellness, making it a core part of a sustainable, inflammation-fighting lifestyle.
Ideal options
Fish and seafood
Skinless poultry
Legumes (beans, lentils, peas)
Tofu and tempeh
Eggs (in moderation)
Herbs and Spices

Many herbs and spices are powerful additions to the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, offering natural ways to reduce inflammation in the body. Packed with antioxidants and beneficial compounds, they help combat oxidative stress and support the body’s defense system.
Common spices like turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, and garlic not only add rich flavor to meals but also deliver anti-inflammatory benefits. These ingredients work by fighting harmful free radicals and supporting immune function, making them valuable tools in maintaining overall health.
Including a wide range of herbs and spices into your cooking is a simple yet effective way to strengthen the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. These natural seasonings enhance both taste and nutrition, helping to protect the body from chronic inflammation and contributing to long-term wellbeing.
Popular choices
Turmeric (curcumin is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent)
Ginger
Garlic
Cinnamon
Rosemary
Cayenne pepper
Foods to Avoid on an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
To reduce inflammation, steer clear of:
Processed and fried foods often contain harmful trans fats, artificial additives, and preservatives that may trigger or worsen inflammation in the body. These types of foods are discouraged in the Anti-Inflammatory Diet because they can disrupt cellular health and contribute to chronic disease over time.
Refined sugars, commonly present in sugary beverages, candies, and sweet pastries, can lead to an increased inflammatory response. The Anti-Inflammatory Diet advises limiting these sugars as they can spike insulin levels and aggravate inflammation-related conditions.
Refined carbohydrates such as white bread, white rice, and regular pasta can rapidly raise blood sugar levels. This can lead to heightened inflammatory activity, which is why the Anti-Inflammatory Diet promotes whole grains instead of refined options.
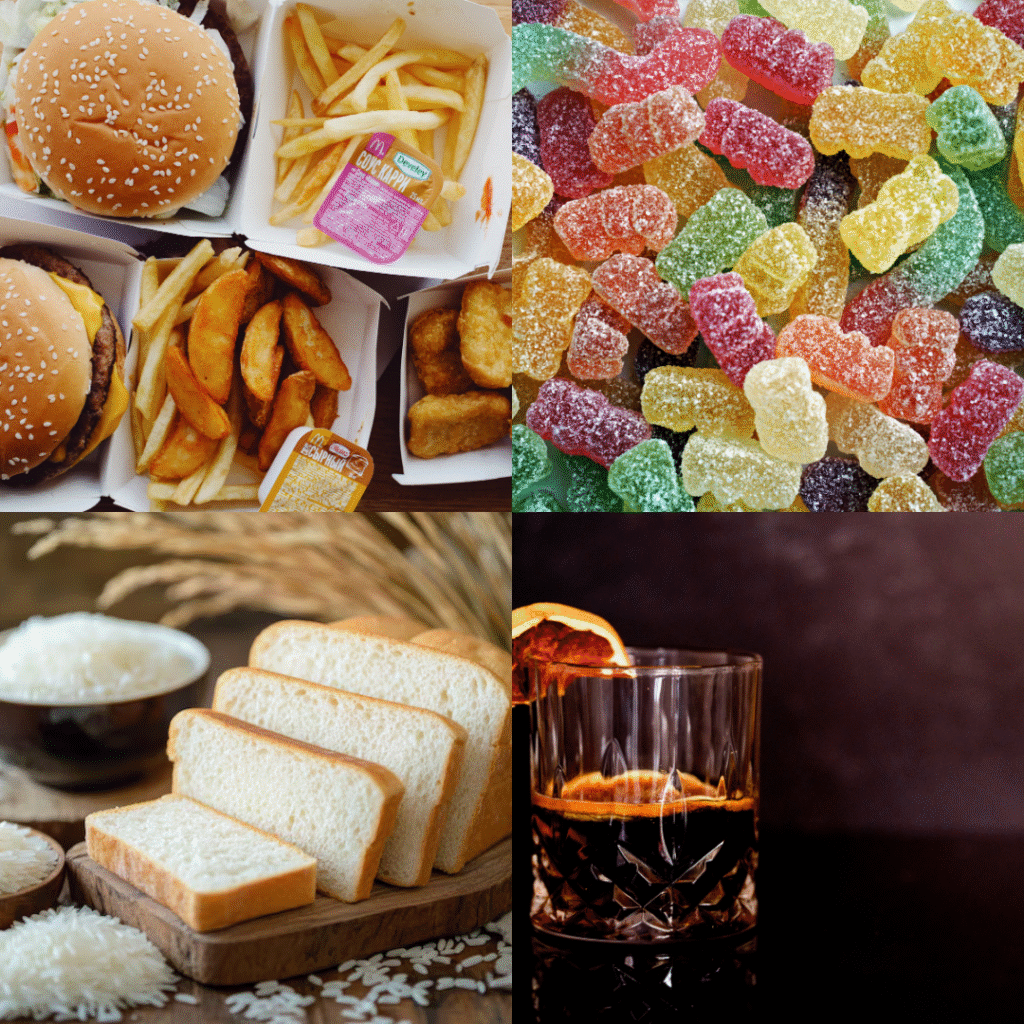
Excessive intake of saturated and trans fats, which are often found in fast food, margarine, and many packaged baked goods, may contribute to chronic inflammation and long-term health complications. The Anti-Inflammatory Diet encourages replacing these fats with healthier alternatives.
Consuming too much alcohol can disrupt gut function and raise markers of inflammation in the body. The Anti-Inflammatory Diet recommends moderate or limited alcohol intake to help maintain a balanced and healthy inflammatory response.
Benefits of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Following this diet provides a range of health benefits:
Reduction of Chronic Inflammation
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet has been consistently associated with a marked reduction in chronic inflammation, as supported by numerous scientific studies. This dietary approach emphasizes the intake of foods rich in antioxidants, essential vitamins, and beneficial nutrients that work synergistically to calm the immune system and reduce inflammatory activity. Regular consumption of anti-inflammatory foods can lower harmful markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), both of which are indicators of inflammation that contribute to the development of long-term illnesses. Embracing the Anti-Inflammatory Diet as a lifestyle choice not only helps defend the body against chronic disease but also enhances overall vitality and resilience.
Promotion of Heart Health
One of the primary advantages of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet is its significant support for cardiovascular wellbeing. This dietary pattern is particularly effective in lowering levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol—commonly known as “bad” cholesterol—which is a major contributor to arterial plaque buildup. Along with improved blood lipid profiles, the Anti-Inflammatory Diet enhances vascular function and promotes more efficient blood flow throughout the body. These combined effects reduce the heart’s workload and help prevent serious health issues such as heart attacks and strokes, making it a strategic, natural way to preserve cardiovascular health over the long term.
Support for Healthy Weight Management
Weight control becomes more manageable with the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, thanks to its emphasis on whole foods and healthy fats that naturally promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction. These nutrient-rich components help to regulate appetite, reduce food cravings, and support more mindful eating habits. By fostering satiety and minimizing the urge to overeat, the Anti-Inflammatory Diet aids in establishing sustainable weight management practices. Furthermore, reducing inflammation through dietary choices contributes to a healthier metabolism and body composition, supporting lasting wellness and energy balance.

Better Regulation of Blood Sugar Levels
A foundational aspect of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet is its inclusion of high-fiber foods that help stabilize blood glucose levels. These foods slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes and dips in energy. Maintaining balanced blood sugar helps reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes—a condition often associated with chronic inflammation. Regular intake of fiber not only supports glycemic control but also strengthens the body’s defense against inflammatory damage. This makes the Anti-Inflammatory Diet a valuable ally in the ongoing effort to maintain healthy metabolic function.
Enhancement of Brain and Cognitive Function
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet plays a critical role in supporting cognitive performance and neurological health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants help shield brain cells from the damaging effects of oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are linked to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. This dietary pattern may reduce the risk of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease by protecting memory, enhancing mental clarity, and preserving brain structure. Following the Anti-Inflammatory Diet provides a proactive and nourishing way to maintain long-term brain health.
Relief from Joint Discomfort and Arthritis Symptoms
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet is particularly beneficial for individuals struggling with joint pain, stiffness, and arthritis. By focusing on anti-inflammatory foods that regulate immune response and reduce internal inflammation, this diet naturally alleviates discomfort in the joints. People who adopt this eating style often report improved mobility, reduced pain, and enhanced quality of life. The anti-inflammatory properties of the diet work to soothe affected areas and support healthier joint function, making it a reliable, non-invasive option for managing arthritis-related issues.
Improved Digestive and Gut Health
Digestive wellness is another key area positively influenced by the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. Foods high in fiber nourish the gut microbiome by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. A healthy and balanced gut environment plays a central role in regulating the immune system and controlling systemic inflammation. By fostering optimal digestive function, the Anti-Inflammatory Diet strengthens the body’s defense mechanisms and enhances nutrient absorption. This dietary approach ensures that digestive health is maintained, contributing to better overall wellbeing and resilience against disease.
Sample Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan
| Meal | Menu |
| Breakfast | Oatmeal topped with fresh blueberries, flaxseeds, and a drizzle of honey |
| Green tea | |
| Lunch | Grilled salmon salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, avocado, walnuts, and olive oil vinaigrette |
| Snack | Carrot sticks with hummus |
| Dinner | Quinoa bowl with roasted vegetables (broccoli, bell peppers, sweet potatoes), chickpeas, and turmeric-spiced dressing |
| Dessert | Fresh strawberries or an apple |
Tips for Success on the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Plan Your Meals Thoughtfully: One of the most effective strategies for successfully following the Anti-Inflammatory Diet is planning your meals in advance. Thoughtful meal planning helps eliminate the temptation to make impulsive food choices, which often leads to the consumption of processed and inflammation-promoting items. By organizing your meals ahead of time, you can ensure a consistent intake of fresh, nutrient-dense foods that align with anti-inflammatory principles and support long-term health.
Cook Nutritious Meals at Home Frequently: Preparing your own meals at home plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. Home cooking gives you complete control over the ingredients you use, making it easier to avoid harmful additives, excessive sodium, and unhealthy fats often found in restaurant or packaged foods. This approach ensures that your meals remain wholesome, clean, and in line with your anti-inflammatory lifestyle.
Opt for Organic Produce When Possible: Including organic fruits and vegetables into your Anti-Inflammatory Diet can offer added health benefits. Organic produce is generally grown without synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers, which may help reduce your body’s exposure to inflammation-triggering toxins. Additionally, organic foods are often higher in antioxidants, which are vital in protecting your body from oxidative stress and supporting the anti-inflammatory response.
Maintain Proper Hydration Daily: Staying well-hydrated is an essential yet often overlooked part of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. Consuming adequate amounts of clean, fresh water helps your body flush out toxins, aids in digestion, and ensures that your cells perform optimally. Proper hydration also supports the body’s natural detoxification systems, which are important in managing inflammation and promoting internal balance.
Include Stress-Reduction Techniques: To fully benefit from the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, it’s important to address lifestyle factors like stress, which can significantly increase inflammation levels in the body. Practicing mindfulness, engaging in yoga, or setting aside time for meditation can effectively reduce stress and enhance the impact of your dietary efforts. Combining nutritional choices with emotional wellness strategies creates a more comprehensive approach to managing inflammation.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Consistent physical movement complements the Anti-Inflammatory Diet by helping to lower systemic inflammation and improve overall health. Exercise boosts circulation, enhances mood, and strengthens the immune system—all of which contribute to a healthier internal environment. Whether it’s walking, swimming, or strength training, integrating regular physical activity into your routine magnifies the benefits of your anti-inflammatory eating habits.
Common Myths About the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Myth 1: The Anti-Inflammatory Diet is Just a Fad
Truth: This diet is backed by strong scientific research and promotes a healthy, balanced way of eating.
Myth 2: You Must Give Up All Your Favorite Foods
Truth: Moderation is important—enjoying treats occasionally won’t harm your progress.
Myth 3: The Diet is Too Expensive
Truth: Many anti-inflammatory foods, such as beans, oats, and seasonal vegetables, are budget-friendly and accessible.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation is a hidden threat that can quietly damage your health over time. The good news is that by embracing the Anti-Inflammatory Diet, you provide your body with the essential nutrients it needs to fight inflammation naturally. This diet emphasizes eating whole, colorful, and nutrient-dense foods while minimizing processed items, sugary treats, and unhealthy fats.
Taking simple steps toward the Anti-Inflammatory Diet can have a powerful impact on your wellbeing. Start small, have fun trying new recipes, and pay attention to how your body feels. With consistency, you’ll likely experience increased energy, less pain, improved mood, and a stronger immune system.
Remember, food is medicine. Let the Anti-Inflammatory Diet be your natural prescription for a healthier, happier life—one meal at a time. By nourishing your body properly, you can protect your health and enjoy lasting benefits.
FAQs
- What is the Anti-Inflammatory Diet ?
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet is a way of eating that focuses on whole, natural foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins. These foods help reduce inflammation in the body and support overall health. - How does the Anti-Inflammatory Diet help with chronic diseases ?
This diet lowers inflammation, which is linked to many chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and Alzheimer’s. By calming the immune system, it helps protect against long-term damage. - Can I follow the Anti-Inflammatory Diet if I’m vegetarian or vegan ?
Yes. The diet is flexible and can be adapted to plant-based lifestyles. Many anti-inflammatory foods—like leafy greens, berries, nuts, seeds, and legumes—are naturally plant-based. - Are there any foods I should avoid on the Anti-Inflammatory Diet ?
Yes. It’s best to limit processed foods, added sugars, refined carbs, and unhealthy fats, as they can trigger inflammation and reduce the benefits of the diet. - How soon will I notice results on the Anti-Inflammatory Diet ?
Some people notice more energy, better digestion, and reduced pain within a few weeks. Long-term benefits like reduced disease risk may take more time and consistency.


